
SYMoyaNetwork
Based on the network abstraction of secondary encapsulation of Moya. Maintain the same usage method of Moya and extend Moya’s TargetType implements commonly used data parsing, supporting: ObjectMapper, Codable, SwiftyJSON, Developer there is no need to write boilerplate code for data parsing. You only need to care about what kind of data you want and select the data type. SYMoyaNetwork has done all this. SYMoyaNetwork also implements network caching, and configure common caching strategies to only implement the desired caching strategy. Response will perform cache synchronization according to the policy. Developers no longer need to spend a lot of time doing such work. SYMoyaNetwork allows data requests Become simple, less developers write boilerplate code, more time to focus on business.
For more information, please see the Doc:
What
Maybe you will use Moya as an abstraction for network requests, like most iOS developers, Moya is a great framework that standardizes your data requests and allows you to complete data requests simply enough. SYMoyaNetwork is based on Moya secondary encapsulation, it does not change the way of using Moya, it is just a further expansion and more friendly encapsulation of Moya.
Maybe you would use Moya to write the request like this:
provider = MoyaProvider<GitHub>()
provider.request(.zen) { result in
switch result {
case let .success(moyaResponse):
let data = moyaResponse.data
let statusCode = moyaResponse.statusCode
// do something with the response data or statusCode
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
When the data request is completed, we need to manually convert moyaResponse into the data object we want. For example, when using ObjectMapper as the data model, we need to do it every time When returning a response, you need to convert moyaResponse into a BaseMappable object. Maybe you can encapsulate a unified method to do this, but you still need to manually call some of these conversion methods, which will make the user do this tediously. And tasteless work, so SYMoyaNetwork has done such a job, you only need to care about the data you want to get, SYMoyaNetwork will give you the data you want to return, For example, when using ObjectMapper as the data model, we can obtain the data object like this
provider = SYMoyaProvider<GitHub>()
/// Note: `BaseMappable `here is the data type in which you implement `BaseMappable`, such as a `Class` or `Struct` or `Other`
provider.responseObject(.zen) { (response: SYMoyaNetworkDataResponse<BaseMappable>) in
switch response.result {
case let .success(mappable):
// The mappable will be the data you want to get, you can use it directly, you don’t need to do any conversion
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
Now using SYMoyaNetwork, you no longer need to worry about how to convert the response into the data you want, you only need to care about the data you want, SYMoyaNetwork has already done all this.
SYMoyaNetwork provides common data type parsing for a variety of data types, such as: JSON, String, Image, ObjectMapper, Codable, SwiftyJSON, when used You only need to care about the data you want to get, and you don’t need to care about the rest. SYMoyaNetwork has already prepared the Response of Moya Analysis, you only care about your business implementation.
SYMoyaNetwork not only converts the Response of Moya, but more importantly, in Moya SYMoyaNetwork has helped you with network caching. In most applications, network caching is very important. It can make your App display faster. Data can save data traffic for users. It can be said that it is a very important decision at the network layer. Therefore SYMoyaNetwork provides the implementation of commonly used network caching strategies. Please refer to [Data Caching](https://raw.github.com/Shannon-Yang/SYMoyaNetwork/master/### data cache).
SYMoyaNetwork supports Combine, and also supports RxSwift, ReactiveSwift and other commonly used responsive frameworks.
SYMoyaNetwork also supports chain requests and batch requests. In most business situations, we may have a batch of requests to send, or related chain requests. also provides these Function can be implemented easily and quickly, refer to: [Chain Request] (###Chain Request) and [Batch Request] (### Batch Request).
Feature
- Support: Codable, SwiftyJSON data parsing, developers only need to care about the data you want to get.
- Extend the
TargetTypeof Moya and addtimeoutInterval,cdnURL,allowsCellularAccess,cachePolicyand other attributes. - Support data caching (disk and memory) and implement data caching strategies.
- Support China Request.
- Support Batch Request.
- Supports Combine, and also supports RxSwift, ReactiveSwift and other commonly used responsive frameworks.
- Supports
Concurrencyasynchronous calls. - Supports request log output, and request data information is clear at a glance.
Tip
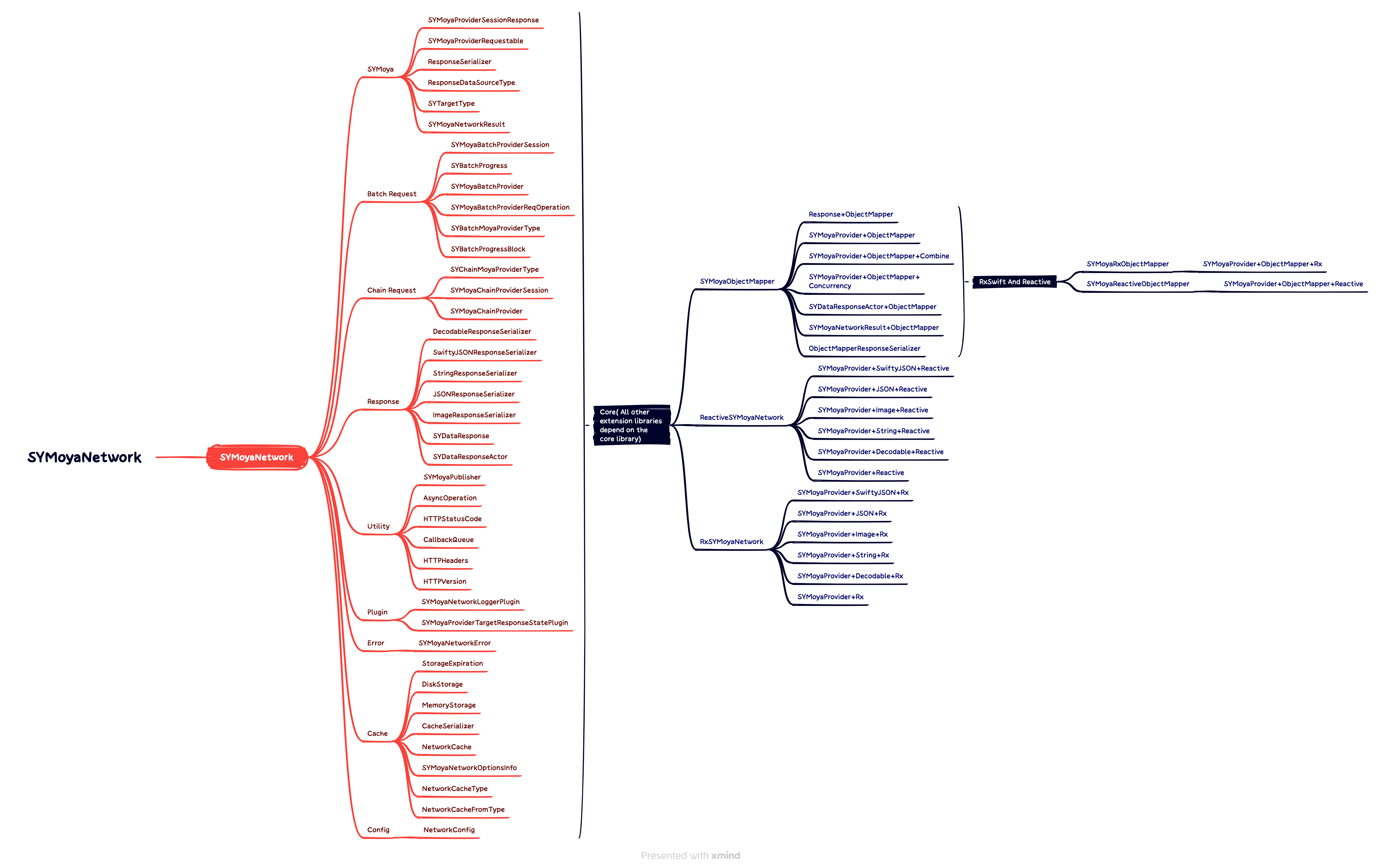
SYMoyaNetwork In order to support different types of data parsing, different types of data parsing are split into different Framework packages. All parsing data packages depend on the core Core package. Developers can choose the parsing to use. Type to install, for example: use RxSwift to directly install the SYMoyaObjectMapper package, if you also need to use ObjectMapper as data parsing, then you can install SYMoyaRxObjectMapper.
Install
Swift Package Manager
To use Apple's Swift Package Manager integration, add the following as a dependency to your Package.swift:
.package(url: "https://github.com/Shannon-Yang/SYMoyaNetwork", .upToNextMajor(from: "2.0.0"))
Then specify SYMoyaNetwork dependency for your Taeget. Here is a PackageDescription instance:
// swift-tools-version:5.3
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "MyPackage",
products: [
.library(
name: "MyPackage",
targets: ["MyPackage"]),
],
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/Shannon-Yang/SYMoyaNetwork", .upToNextMajor(from: "2.0.0"))
]
)
CocoaPods
Add SYMoyaNetwork to your Podfile:
pod 'SYMoyaNetwork', '~> 2.0'
# or
pod 'SYMoyaNetwork/SYMoyaReactiveObjectMapper', '~> 2.0'
#or
pod 'SYMoyaNetwork/SYMoyaRxObjectMapper', '~> 2.0'
#or
pod 'SYMoyaNetwork/SYMoyaObjectMapper', '~> 2.0'
#or
pod 'SYMoyaNetwork/ReactiveSYMoyaNetwork', '~> 2.0'
#or
pod 'SYMoyaNetwork/RxSYMoyaNetwork', '~> 2.0'
then run pod install.
In any file where you want to use SYMoyaNetwork, use import SYMoyaNetwork to import the framework.
Carthage
Carthage users can point to this repository and use their preferred build framework, SYMoyaNetwork
Add the following code to your Cartfile:
github "Shannon-Yang/SYMoyaNetwork"
Then run carthage update --use-xcframeworks.
If this is your first time using Carthage in a project, you will need to take some additional steps, which are described in Carthage explain.
NOTE: At this time, Carthage does not provide a way to build only specific repository submodules. All submodules and their dependencies will be built with the above command. However, you don't need to copy frameworks you aren't using into your project. For instance, if you aren't using
ObjectMapper, feel free to delete that framework along withObjectMapperfrom the Carthage Build directory aftercarthage updatecompletes.
Manual
- Open a terminal and
cdto the top directory of your project. If your project is not initialized as a git repository, run the following command:
$ git init
- Add
Alamofire&Moya&SYMoyaNetwork& The data model library you want to use, such as ObjectMapper as git submodule:
$ git submodule add https://github.com/Alamofire/Alamofire.git
$ git submodule add https://github.com/Moya/Moya.git
$ git submodule add https://github.com/Shannon-Yang/SYMoyaNetwork
$ git submodule add 'The data model library you want to use, such as ObjectMapper, SwiftyJSON'
- Open the newly created
Alamofirefolder and dragAlamofire.xcodeprojinto your Xcode project navigation. Do the same operation forMoya.xcodeprojunder the Moya folder, do the same operation forSYMoyaNetwork.xcodeprojunder the SYMoyaNetwork folder, and do the same for other data model libraries.
They should be nested beneath the blue project icon of your application, above or below other Xcode groups, it doesn’t matter.
- Verify that the deployment
targetofxcodeprojis consistent with the applicationtargetin your project navigation. - Next, select your application project in the project navigation (blue project icon) and then navigate to the
targetconfiguration window and select the applicationtargetunder theTargetsheading in the sidebar. - In the tab bar at the top of the window, open the "General" panel.
- Click the
+button below theEmbedded Binariesfield. - You will see two different
Alamofire.xcodeprojfolders. Each folder has two different versions ofAlamofire.frameworknested within theProductsfolder.
It doesn’t matter which
Productsfolder you choose, what matters is whether you choose theAlamofire.frameworkabove or below.
- Select
Alamofire.frameworkabove for iOS and below for macOS.
You can verify which one you selected by checking the project's build log. The build target for
Alamofirewill be listed asAlamofire iOS,Alamofire macOS,Alamofire tvOSorAlamofire watchOS.
-
Click the
+button again to add the correct build target forMoyaand do the same forSYMoyaNetwork -
That's it!
These frameworks are automatically added to a copy files build phase as target dependencies, linked frameworks and embedded frameworks, and that's all you need to build on emulators and devices.
Usage
Data Request
Just like using Moya, the usage of SYMoyaNetwork is exactly the same as Moya. You don’t have to worry about its complicated usage.
SYMoyaNetwork provides support for multiple data types such as JSON, String, Image, ObjectMapper, Codable, SwiftyJSON etc. You can use SYMoyaProvider to call the corresponding Response method.
JSON
provider = SYMoyaProvider<GitHub>()
provider.responseJSON(.zen) { (response: SYMoyaNetworkDataResponse<Any>) in
switch response.result {
case let .success(json):
// do something with the response json data. You can use the json object directly without conversion
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
String
provider = SYMoyaProvider<GitHub>()
provider.responseString(.zen) { (response: SYMoyaNetworkDataResponse<String>) in
switch response.result {
case let .success(string):
// do something with the response string data. You can use the string object directly without conversion
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
Image
provider = SYMoyaProvider<GitHub>()
provider.responseImage(.zen) { (response: SYMoyaNetworkDataResponse<Image>) in
switch response.result {
case let .success(image):
// do something with the response image data. You can use the image object directly without conversion
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
ObjectMapper
provider = SYMoyaProvider<GitHub>()
provider.responseObject(.zen) { (response: SYMoyaNetworkDataResponse<T: BaseMappable>) in
switch response.result {
case let .success(mappableObject):
// do something with the response mappableObject data. You can use the mappableObject object directly without conversion
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
Codable
provider = SYMoyaProvider<GitHub>()
provider.responseObject(.zen) { (response: SYMoyaNetworkDataResponse<T: Decodable>) in
switch response.result {
case let .success(codableObject):
// do something with the response codableObject data. You can use the codableObject object directly without conversion
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
SwiftyJSON
provider = SYMoyaProvider<GitHub>()
provider.responseSwiftyJSON(.zen) { (response: SYMoyaNetworkDataResponse<SwiftyJSON.JSON>) in
switch response.result {
case let .success(swiftyjson):
// do something with the response swiftyjson data. You can use the swiftyjson object directly without conversion
case let .failure(error):
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
}
Data Cache
In most business situations, we need to cache the Response returned by the server locally, for example: those resources that have not been updated for a long time or the content that needs to be displayed when the user does not have a network, SYMoyaNetwork has already done this With all this🍯, you only need to set the properties of networkCacheType in SYTarget and configure NetworkCacheOptionsInfo. SYMoyaNetwork has done two kinds of storage, one is memory storage (MemoryStorage) and the other is Disk storage (DiskStorage) needs to pass in storage-related information, such as: diskStorageConfig, memoryStorageConfig etc. For details, please refer to NetworkCacheType.NetworkCacheOptionsInfo. The specific example code is as follows:
var networkCacheType: NetworkCacheType {
return .cache(networkCacheOptionsInfo: .init())
}
The networkCacheOptionsInfo used by default is the default configuration in NetworkConfig. You can also customize the configuration. You only need to initialize the customized networkCacheOptionsInfo object. When the networkCacheType return type is cache, when the request is completed, it will Use this parameter to verify whether the cache conditions are met. If the cache conditions are met, whether it is a Get, Post or other request, the data will be cached automatically based on the cache information.
SYMoyaProvider provides responseCodableObject, responseObject<T: BaseMappable>, responseSwiftyJSON and other methods. In each method, there is a parameter such as responseDataSourceType. This parameter Mainly the response type of data return. Currently, responseDataSourceType is divided into 5 data return types: server, cache, cacheIfPossible, cacheAndServer, and custom.
server:Get data directly from the server, cached data will not be retrievedcache:If there is a cache, get the data directly from the cache and make a callback. Thesuccessresult will be called back. If there is no cache, thefailureresult will be called back and the correspondingerrorinformation will be returned. No network request will be initiated, only Will be retrieved from cache.cacheIfPossible:If there is a cache, the data will be obtained directly from the cache. If the cache acquisition is successful, asuccesscallback will be performed. If the cache acquisition fails, a network request will be initiated. After the network request is successful, asuccesscallback will be performed. After the request fails, asuccesscallback will be performed. Make afailurecallback.cacheAndServer:If the current interface has a cache, it will first obtain the cache data and then make a callback, then initiate a network request, and then call back again.custom:The callback of the custom mode needs to implement theResponseDataSourceCustomizableprotocol, which will first obtain the cache data from the cache. After obtaining the cache data, the current cache number will be called back through theshouldSendRequestmethod, which can be judged by the callback cache data. , you need to call back whether the cache needs to be updated through theshouldUpdateCachemethod. This data callback mode is more commonly used for requests to obtain relatively large amounts of data.
The scenario of
customis as follows. For example: we have a book with a lot of book details. When we obtain the book details for the first time, a more clever approach is to put the current book details into The book details of this book are cached locally. The next time you open the app, the cached data of this book will be displayed first, and then the latest data of the book details will be requested and the local cache will be updated. This will indeed achieve the desired effect, but It is not the optimal solution. Under normal circumstances, if a complete request for book details overwrites the local cache, since the book details data may be relatively large, the network request response time will be very long, and the user's data traffic will also be wasted, so A better solution is to only request some basic information of the current book, use some key fields of the basic information to determine whether the current locally cached book data is the latest, and then determine whether the local cache needs to be updated. If the detailed data of the book is The latest, then there will be no need to request data, such asversionand other fields in the basic information. You can passversionand other fields to the server to verify whether the current cache is the latest. If the current cache is not the latest Then initiate a network request to request the latest book details data. This can not only display the data to the user first, but also save user traffic and reduce requests for this huge data when there is no need to update the data.
Batch Request
In some cases, we may need to send a batch of network requests. SYMoyaNetwork provides batch initiating network request operations. SYMoyaBatchProviderSession is mainly used to initiate batch network request operations. Before initiating network requests, it is necessary to initialize and implement SYBatchMoyaProviderType Array object, by default SYMoyaBatchProvider has implemented SYBatchMoyaProviderType. During batch requests, SYMoyaBatchProviderSession maintains a SYMoyaBatchProvider request array. After all requests are completed, an array of SYMoyaProviderSessionResponse will be returned.
Note: During the batch request process, as long as one of the requests fails, the entire Provider will call back the
failuremethod. Only after all requests are successful will thesuccessbe called back.
eg:
var session: SYMoyaBatchProviderSession?
let provider = SYMoyaBatchProvider<HTTPBinDynamicData>(targetTypes: [.getDelay(delay: 1), .stream(n: 1)])
let provider2 = SYMoyaBatchProvider<HTTPBinResponseFormats>(targetTypes: [.brotli, .json, .gzipped])
session = SYMoyaBatchProviderSession(providers: [provider, provider2])
session?.request { [weak self] progress in
// do something with the response batch data. You can use the batchData directly without conversion
} completion: { [weak self] result in
// this means there was a network failure - either the request
// wasn't sent (connectivity), or no response was received (server
// timed out). If the server responds with a 4xx or 5xx error, that
// will be sent as a ".success"-ful response.
}
Chain Request
Used to manage interdependent network requests, it can actually eventually be used to manage multiple topologically sorted network requests.
For example, we have a business that requires users to first send the registered API when registering:
- If the registration is successful, send the API to read the user information. Moreover, the API that reads user information needs to use the user id returned by successful registration.
- If registration fails, the API for reading user information will not be sent.。
eg:
let chainProvider = SYMoyaChainProvider(targetType: HTTPBinAuth.bearer) { progress in
debugPrint("🏃🏻♀️🏃🏻♀️🏃🏻♀️🏃🏻♀️----> \(progress) <---- < Class: \(type(of: self)) Function:\(#function) Line: \(#line) >🏃🏻♀️🏃🏻♀️🏃🏻♀️🏃🏻♀️")
}
SYMoyaChainProviderSession.request(chainMoyaProviderType: chainProvider) { response in
let targetType = response.targetType
let result = response.result
switch targetType {
case HTTPBinAuth.bearer:
let json = result.serializerSwiftyJSON().value
let authenticated = json?["authenticated"].boolValue ?? false
if authenticated {
return SYMoyaChainProvider(targetType: HTTPBinDynamicData.getDelay(delay: 1))
}
case HTTPBinDynamicData.getDelay:
let responseString = result.serializerStringDataResponse(atKeyPath: nil)
self.contentLabel.text = responseString.value
self.contentLabel.isHidden = false
self.indicator.stopAnimating()
default:
break
}
return nil
} completion: {
self.indicator.stopAnimating()
debugPrint("🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥----> <---- < Class: \(type(of: self)) Function:\(#function) Line: \(#line) >🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥")
}
License
SYMoyaNetwork is released under an MIT license. See License.md for more information.
GitHub
| link |
| Stars: 5 |
| Last commit: 1 week ago |
Dependencies
Release Notes
1.add SYMoyaProviderTargetResponseStatePlugin 2.SYMoyaProvider add 'responseState' 3.override super func 4.SYMoyaProviderDelegate add target parameter 5. some fix
Swiftpack is being maintained by Petr Pavlik | @ptrpavlik | @swiftpackco | API | Analytics