NetworkKit
A light abstraction layer on top of URLSession, NetworkKit provides a clear way to organise your network API requests.
⚠️ Warning: This package is under active development and is not considered ready for production use.
Network
The Network protocol is a way to share common properties and settings between requests that use the same service. You can use a Network to set common properties such as a base URL, headers, or encoding/decoding settings.
class MoviesNetwork: Network {
let baseURL: URL = .init(string:"https://api.themoviedb.org/3/")!
}
Consider implementing your
Networkas anObservableObjectand passing it through your SwiftUI view hierarchy with@EnvironmentObject.
Requests
Create requests for a Network by implementing the NetworkRequest protocol.
struct FetchMovies: NetworkRequest {
let method: HTTPMethod = .get
let path: String = "discover/movie"
}
Now you can perform this request on your network by using the request(on: Network) method.
FetchMovies().request(on: moviesNetwork)
The request(on: Network) method returns a Combine Publisher that publishes Data once the request is complete.
Responses
The response type of a NetworkRequest can be customised using the Response associated type.
struct FetchMovies: NetworkRequest {
let method: HTTPMethod = .get
let path: String = "discover/movie"
struct Response: Decodable {
let page: Int
let results: [Movie]
}
}
Note: If you have a model that matches your response type you can just assign it directly to the associated type by using
typealias Response = CustomResponseTypein your request.
If the Response type is Decodable the response will be automatically decoded and the Publisher returned from request will instead publish that decoded response.
FetchMovies()
.request(on: moviesNetwork)
.assertNoFailure()
.sink { (movies) in
print(movies.results)
}
Note: By default, NetworkKit supports
Decodable,UIImage, andDataresponse types. You can support custom response types by implementingresponse(on: Network, for: Data) -> Responsein yourNetworkRequest.
Parameters
Provide parameters for your requests by implementing the parameters property on your NetworkRequest as an encodable object.
struct FetchMovies: NetworkRequest {
let method: HTTPMethod = .get
let path: String = "discover/movie"
let parameters: Parameters
struct Parameters: Encodable {
let sortBy: String
}
}
You can customise the encoding destination of your parameters by implementing the encoding property on the request (url and json encoding is supported).
Note: You can customise
Dateencoding and decoding by implementing thedateEncodingStrategyanddateDecodingStrategyproperties on yourNetwork.
Error Handling
The publisher returned from Network.request publishes a NetworkError whenever an error occurs. NetworkError is an enum that contains two cases: local and remote.
- Local errors are errors that have occured locally on the device (such as encoding errors or connection issues).
- Remote errors contain an error returned from a remote HTTP service. You can customise the type of this error by setting the
RemoteErrorassociated type of yourNetwork.
class MoviesNetwork: Network, ObservableObject {
let baseURL: URL = .init(string:"https://api.themoviedb.org/3/")!
struct RemoteError: Decodable {
let code: Int
let message: String
}
}
If the RemoteError type is Decodable the data from the failed request will be automatically decoded to that type.
FetchMovies()
.request(on: moviesNetwork)
.catch { error in
switch error {
case .local(let localError):
print(localError)
case .remote(let remoteError):
print(remoteError.message)
}
}
Note: If your
RemoteErrortype doesn't implementDecodableyou can map the returned data directly by implementingNetwork.errorContent(for: HTTPURLResponse, data: Data) -> RemoteError.
Preview Modes
A Network can show mock preview data from local assets. You can set the preview mode of your Network by calling the preview(_: NetworkPreviewMode) method.
If the preview mode is set to always the network will search the app for an asset with a name matching the full path of the request without the scheme (https://api.themoviedb.org/3/movies becomes api.themoviedb.org/3/movies).
Add JSON files for your Decodable requests and image assets for your UIImage requests. You can also use any data asset for other response types. You can use asset catalog groups with Provides Namespace enabled to organise your preview assets.
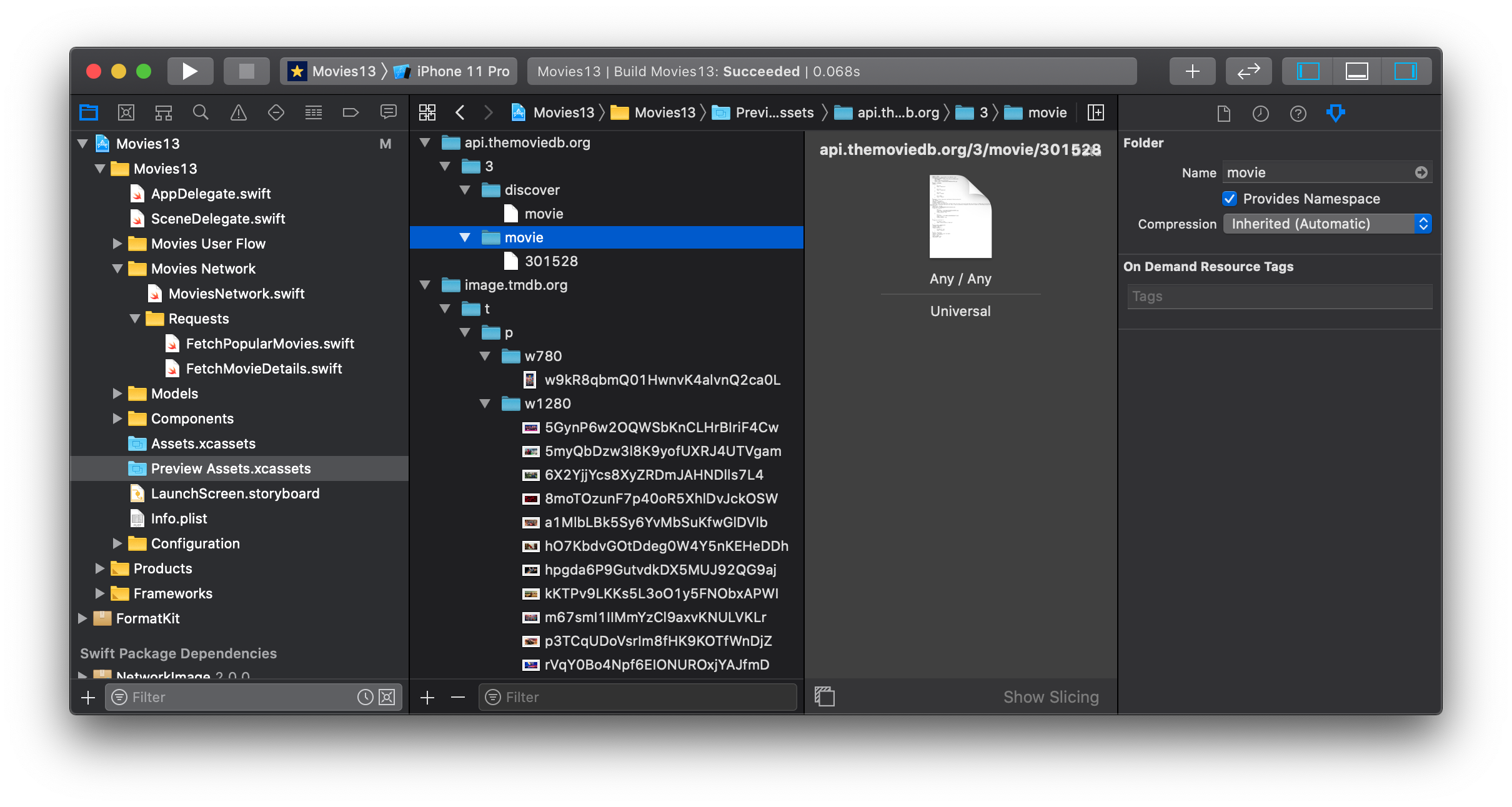
Note: By default, a
Networkwill use theautomaticpreview mode which will detect when the network is being used in an Xcode preview and use thealwaysmode in that case, otherwise it with use thenevermode.
If you've passed your Network through your SwiftUI view layer using environmentObject, it's easy to override the network with a preview network in your Xcode Previews.
struct MoviesScreen_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
MoviesScreen()
.environmentObject(MoviesNetwork().preview(.always))
}
}
You can also get mock data directly from your preview assets by using the NetworkRequest.preview(on: Network) method.
struct MovieSummaryRow_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
MovieSummaryRow(movieSummary: try! FetchMovieSummary(id: 42).preview(on: MoviesNetwork()))
}
}
GitHub
| link |
| Stars: 3 |
| Last commit: 3 years ago |
Related Packages
Release Notes
Swiftpack is being maintained by Petr Pavlik | @ptrpavlik | @swiftpackco | API | Analytics